! python --versionPython 3.11.14Using an Active Generalized Filter agent for control
Kobus Esterhuysen
January 21, 2026
January 22, 2026
In this project we apply the established Active Inference (AIF) modeling approach (making use of Bond Graphs, Generalized Filters, and Generalized Coordinates of Motion) to an electric system. The latter is not a complicated system. Also, the generalized coordinates part of the experiment needs more tuning.
A few coding conventions:
See Part 1
N/A. We will not make use of collected data for training. Training happens online during simulation.
N/A. We will not make use of collected data for training. Training happens online during simulation.
Please see the description from section 1: BUSINESS UNDERSTANDING
This section attempts to answer three important questions:
The voltage across the capacitor
The decision involves what control current should be injected into the circuit during each time step,
A source of uncertainty is the disturbance current
The state at time envir) is given by
q3 code variablep6 code variableThe decision variables represent what we control.
The environment is steered by decisions/actions
a5 code variableThe exogenous information is not controllable by the agent.
where
v7 code variableTo find the next state for each time step, the generative process starts with the transition function
To find the observation generated by the external state of the generative process for each time step, the generative process starts with the generation function
where
ALPHA = 0.6
ENV_WIDTH = 4. ## 8.
AGT_WIDTH = 2.
AGT_LINESTYLES = ['-', '--', '-.', ':'] ## for agent
ORANGE_HUE_BY_SATURATION = [
"#FFA500", ## 100% bright orange
"#FFB347", ## 80% light vivid orange
"#FFD580", ## 60% softer pastel orange
"#FFE5B4" ## 40% light faded orange
]
ORANGE_HUE_BY_BRIGHTNESS = [
"#FFA500", ## 100% pure bright orange
"#FFC04D", ## 80% light orange
"#FFD699", ## 60% pastel orange
"#FFE5CC" ## 40% very pale orange
]
ORANGE_HUE = ORANGE_HUE_BY_BRIGHTNESS
styles = {
#### envir
"a": {
"color": "crimson",
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"xˣ[0]": {
"color": "black",
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"xˣ[1]": {
"color": "darkgrey",
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"vˣ[0]": {
"color": "blue",
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"vˣ[1]": {
"color": "dodgerblue",
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"y[0]": {
"color": ORANGE_HUE[0],
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"y[1]": {
"color": ORANGE_HUE[1],
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"y[2]": {
"color": ORANGE_HUE[2],
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"y[3]": {
"color": ORANGE_HUE[3],
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": ENV_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
#### agent
"μ_x[0]": {
"color": "black",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[0],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_x[1]": {
"color": "black",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[1],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"v[0]": {
"color": "blue",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[0],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"v[1]": {
"color": "blue",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[1],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_v[0]": {
"color": "dodgerblue",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[0],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_v[1]": {
"color": "dodgerblue",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[1],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_y[0]": {
"color": "orange",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[0],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_y[1]": {
"color": "orange",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[1],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"μ_y[2]": {
"color": "orange",
"linestyle": AGT_LINESTYLES[2],
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
},
"F": {
"color": "#9400D3", ## vivid deep violet
"linestyle": "-",
"linewidth": AGT_WIDTH,
"alpha": ALPHA
}
}
## Precision matrices
# def expand_diag(val, size):
# return np.diag([val for _ in range(size)])#### time
tT = 10000 ## end t in ms
# Δt = 1. ## ms
Δt = .5 ## ms
ts = np.arange(0, tT, Δt) ## time steps
T = len(ts)
#### dimensionsionality of vectors
B = 1 ## number of dims for autonomous state vˣ/v
C = 2 ## number of dims for state xˣ/μ_x
D = 1 ## number of dims for observation y/μ_y
A = 1 ## number of dims for action a
M = 3 ## number of dims for embedding (generalized coordinates of motion)
#### noise
def white_noise(scale=1e-1, size=1):
return np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=scale, size=size)
## white noise
σˣ2_x = 0.001
σˣ2_y = 0.001
_n_x = white_noise(scale=np.sqrt(σˣ2_x), size=(T,C))
_n_y = white_noise(scale=np.sqrt(σˣ2_y), size=(T,D))
## colored noise via AR(1) filters
_ω_x = np.zeros((T, C))
_ω_y = np.zeros((T, D))
α, β = 0.95, 0.10 ## process noise correlation
γ, δ = 0.90, 0.05 ## measurement noise correlation
## configure colored noise to be white again
## α, β = 0.00, 1.00 ## process noise correlation
## γ, δ = 0.00, 1.00 ## measurement noise correlation
for t in range(0, T - 1):
_ω_x[t] = α*_ω_x[t-1] + β*_n_x[t]
_ω_y[t] = γ*_ω_y[t-1] + δ*_n_y[t]
#### exogenous functions
def f_const(t, A=0.0, **kwargs):
t_arr = np.asarray(t)
val = A * np.ones_like(t_arr, dtype=float)
return float(val) if np.isscalar(t) else val
def f_cos(t, A=1.0, θ1=0.0):
t_arr = np.asarray(t, dtype=float)
val = A * np.cos(θ1 * t_arr)
return float(val) if np.isscalar(t) else val
def f_pulses(t, **kwargs):
"""
Sum of rectangular pulses defined in physical time.
kwargs:
'amps' : list/array of amplitudes [A1, A2, ...]
't_ons' : list/array of start times [t_on1, t_on2, ...]
't_offs' : list/array of end times [t_off1, t_off2, ...]
"""
amps = np.asarray(kwargs['amps'], dtype=float)
t_ons = np.asarray(kwargs['t_ons'], dtype=float)
t_offs = np.asarray(kwargs['t_offs'], dtype=float)
t_arr = np.asarray(t, dtype=float)
val = np.zeros_like(t_arr, dtype=float)
for A, t_on, t_off in zip(amps, t_ons, t_offs):
val += A * (np.heaviside(t_arr - t_on, 0.0) - np.heaviside(t_arr - t_off, 0.0))
return float(val) if np.isscalar(t) else val
def f_lines(t, **kwargs):
"""
Piecewise-linear signal defined by points (t_i, y_i).
kwargs:
'y_pts' : list/array of values [y0, y1, ..., yN]
't_pts' : list/array of time points [t0, t1, ..., tN]
For t between t_i and t_{i+1}, returns the straight line
interpolating between (t_i, y_i) and (t_{i+1}, y_{i+1}).
For t < t0 returns y0, for t > tN returns yN.
"""
y_pts = np.asarray(kwargs['y_pts'], dtype=float)
t_pts = np.asarray(kwargs['t_pts'], dtype=float)
if t_pts.ndim != 1 or y_pts.ndim != 1 or t_pts.size != y_pts.size:
raise ValueError("t_pts and y_pts must be 1D arrays of the same length")
t_arr = np.asarray(t, dtype=float)
## use numpy's 1D linear interpolation
val = np.interp(t_arr, t_pts, y_pts)
return float(val) if np.isscalar(t) else val
rng = np.random.default_rng(1234)
## --- Option 1: White Gaussian noise with std σ ---
def f_normal(t, **kwargs):
"""
Gaussian white noise with std = A*sigma, mean = 0.
Works for scalar or array t.
Expects kwargs: 'A', 'sigma'.
"""
A = kwargs.get('A', 1.0)
sigma = kwargs.get('sigma', 1.0)
t_arr = np.asarray(t)
noise = rng.normal(loc=0.0, scale=A * sigma, size=t_arr.shape)
return float(noise) if np.isscalar(t) else noise
## --- Option 2: Uniform noise in [-A, A] ---
def f_uniform(t, **kwargs):
"""
Uniform white noise in [-A, A].
Works for scalar or array t.
Expects kwargs: 'A'.
"""
A = kwargs.get('A', 1.0)
t_arr = np.asarray(t)
# random in [0, 1) with same shape as t
u = rng.random(size=t_arr.shape)
noise = (2 * A) * (u - 0.5)
return float(noise) if np.isscalar(t) else noise(array([0.00694002, 0.00310657]), array([-0.00158543]))#### envir
θˣ_x = {
'C3': 5.0,
'R2': 2.0,
'L6': 1.0,
'R_a': 1e-3 ## for now
}
def f_E(_xˣ, _vˣ, _a=[0], θˣ_x=θˣ_x): ## transition function for Envir
C3 = θˣ_x['C3']
R2 = θˣ_x['R2']
L6 = θˣ_x['L6']
q3, p6 = _xˣ
v7 = _vˣ[0] if np.ndim(_vˣ) else _vˣ
a5 = _a[0] if np.ndim(_a) else _a
# t1_num = 1; t1_den = C3*R6
# t2_num = 1; t2_den = R6
# t3_num = 1; t3_den = R6
# dq3 = -(t1_num/t1_den)*q3 + (t2_num/t2_den)*v5 + (t3_num/t3_den)*a1
dq3 = +(1/L6)*p6 - v7 - a5
dp6 = -(1/C3)*q3 - (R2/L6)*p6 + R2*v7 + R2*a5
return np.array([dq3, dp6], dtype=float) # shape (2,)
def g_E(_xˣ, _vˣ=None): ## generation function for Envir
q3 = _xˣ[0] if np.ndim(_xˣ) else _xˣ
return np.array([
(1 / θˣ_x['C3']) * q3 ## voltage across C3
])
def dy___da(_xˣ, _a, Δt, θˣ_x=θˣ_x):
C3 = float(θˣ_x['C3'])
R_a = float(θˣ_x['R_a']) ## whatever resistance couples a (temp) to the room
return (Δt / (C3 * R_a)) ## scalar gain °C_out / °C_action(array([0.00694002, 0.00310657]), array([-0.00158543]))#### run
_a = np.zeros((T, A))
_xˣ = np.zeros((T, C))
_vˣ = np.zeros((T, B))
_y = np.zeros((T, D))
_a[0] = [0] ## aSf5
_xˣ[0] = [10, 20] ## xˣq3, xˣp6
_vˣ[0] = [-10] ## vˣSf7
_y[0] = [10] ## yVoltage
sources_env = {
'a5': f_pulses,
'v7': f_cos,
}
a5_theta_env = {
'amps' : [30., -30],
't_ons' : [0., 5000],
't_offs': [5000, 1e10],
}
v7_theta_env = {
'A': 10.,
'θ1' : .003,
}
for t in range(0, T - 1):
_vˣ[t+1] = sources_env['v7'](ts[t], **v7_theta_env)
## vˣ[t+1] = sampled_vˣ ## vˣ[t+1] estimated from 1-step ahead historical data
_a[t+1] = sources_env['a5'](ts[t], **a5_theta_env) ## estimated by using current observation from a sensor
#### NEXT STATE
_ẋ = f_E(_xˣ=_xˣ[t], _vˣ=_vˣ[t], _a=_a[t]) + _ω_x[t]
_xˣ[t+1] = _xˣ[t] + _ẋ*Δt ## f is transition function; Euler
#### OBSERVE
_y[t+1] = g_E(_xˣ[t+1]) + _ω_y[t] ## g is generation function
result_env = pd.DataFrame({
't': ts,
'_n_x_0': _n_x[:,0],
'_ω_x_0': _ω_x[:,0],
'_n_y_0': _n_y[:,0],
'_ω_y_0': _ω_y[:,0],
'_a_0': _a[:,0],
'_xˣ_0': _xˣ[:,0], '_xˣ_1': _xˣ[:,1],
'_vˣ_0': _vˣ[:,0],
'_y_0': _y[:,0]
})
print(result_env.head())
## print(result_env.iloc[40:60]) t _n_x_0 _ω_x_0 _n_y_0 _ω_y_0 _a_0 _xˣ_0 _xˣ_1 \
0 0.0 0.023319 0.002332 -0.020052 -0.001003 0.0 10.000000 20.000000
1 0.5 -0.009119 0.001303 -0.017008 -0.001753 0.0 25.001166 -10.999645
2 1.0 -0.006379 0.000600 -0.007018 -0.001928 30.0 14.501995 7.502540
3 1.5 -0.046794 -0.004109 -0.007782 -0.002125 30.0 -1.746429 38.550459
4 2.0 0.001313 -0.003772 -0.033856 -0.003605 30.0 -2.473232 40.175029
_vˣ_0 _y_0
0 -10.000000 10.000000
1 10.000000 4.999231
2 9.999989 2.898646
3 9.999955 -0.351214
4 9.999899 -0.496771 def plot_envir_result(result):
ylabel_size = 12
ylabelx = -0.3
ylabely = 0.3
# fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
grid_rows = 9
## gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[3, 1, 1])
gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[1]*grid_rows)
ax = [fig.add_subplot(gs[i]) for i in range(grid_rows)]
for j, axis in enumerate(ax):
axis.set_xlim(0, tT)
locator = MaxNLocator(nbins=5)
axis.xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
axis.spines['top'].set_visible(False); axis.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
if j < grid_rows - 1:
axis.set_xticklabels([]) ## hide labels but keep tick positions
i = 0
ax[i].set_title(r'Environment', fontweight='bold',fontsize=14)
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_a_0'], **styles['a'], label=r'$\mathbf{a}[0]=a_5(t)$: action Sf_5')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='$^{\\circ}\\mathrm{C}$'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_vˣ_0'], **styles['vˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{v}^*[0]=v_7(t)$: true Sf_7')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='$^{\\circ}\\mathrm{C}$'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_xˣ_0'], **styles['xˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[0]=q_3(t)$: true charge')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='J'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_xˣ_1'], **styles['xˣ[1]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[1]=p_6(t)$: true flux')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='J'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_y_0'], **styles['y[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{y}[0]=y(t)$: obs $e_{C_3}$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='$^{\\circ}\\mathrm{C}$'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_n_x_0'], color='black', linestyle=':', label=r'$n_x$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='J'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_ω_x_0'], color='black', linestyle=':', label=r'$ω_x$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='J'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_n_y_0'], color='orange', linestyle=':', label=r'$n_y$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='$^{\\circ}\\mathrm{C}$'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result['t'], result['_ω_y_0'], color='orange', linestyle=':', label=r'$ω_y$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='$^{\\circ}\\mathrm{C}$'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
## bottom
ticks = ax[-1].get_xticks()
ax[-1].set_xticks(ticks)
## ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-6*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) # micro-seconds
## ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e0*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) # seconds
ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-3*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) # seconds
ax[i].set_xlabel('$\mathrm{Time}\ t\ [\mathrm{seconds}]$', fontweight='bold', fontsize=12)
## plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3) ## Adjust this value as needed
plt.show()
fig.savefig("./ElectricSystem-envir", bbox_inches="tight", dpi=300)
plot_envir_result(result_env)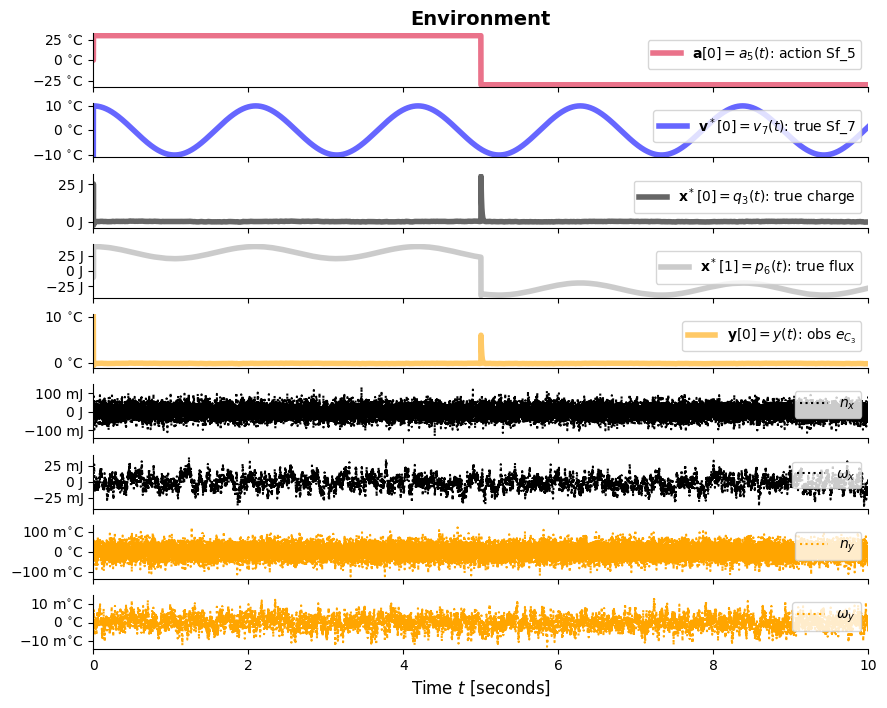
As mentioned before, there is uncertainty in the (colored) process and measurement noise. We will also define models for the time behavior of the disturbance current
For some simplification in what follows, we make use of a quadratic approximation involving the application of a second order Taylor series expansion centered on the mean of the variational density
The calculation of the variational density over the hidden state now only depends on the value of the mean. Effectively this is the same as assuming that
Since the variational density is Gaussian and we plan to evaluate the function at the posterior mode, we substitute all occurences of
#### agent
def f_M(_μₓ, _μᵥ): ## transition function for Model/Agent
C3 = θˣ_x['C3']
R2 = θˣ_x['R2']
L6 = θˣ_x['L6']
q3, p6 = _μₓ
v7 = _μᵥ[0] if np.ndim(_μᵥ) else _μᵥ
# t1_num = 1; t1_den = C3*R6
# t2_num = 1; t2_den = R6
# t3_num = 1; t3_den = R6
# dq3 = -(t1_num/t1_den)*q3 + (t2_num/t2_den)*v5
dq3 = +(1/L6)*p6 - v7
dp6 = -(1/C3)*q3 - (R2/L6)*p6 + R2*v7
return [dq3, dp6]
def g_M(_μₓ, _μᵥ=None): ## generation function for Model/Agent
## q3 = _μₓ[0] if np.ndim(_μₓ) else _μₓ
q3, p6 = _μₓ
return np.array([
(1 / θˣ_x['C3']) * q3 ## voltage across C3
])
def df_M___dμₓ(_μₓ, _μᵥ):
"""
Jacobian of f_M with respect to μₓ = [q3, p6].
Returns a 2x2 numpy array.
"""
C3 = θˣ_x['C3']
R2 = θˣ_x['R2']
L6 = θˣ_x['L6']
return np.array([
[0.0, 1.0 / L6],
[-1.0 / C3, -R2 / L6],
])
def dg_M___dμₓ(_μₓ, _μᵥ=None):
## ensure 1D state of length 2
_μₓ = np.asarray(_μₓ).reshape(2,)
## dy/dq3 = 1/C3, dy/dp6 = 0
return np.array([[1.0 / θˣ_x['C3'], 0.0]]) ## shape (1, 2)
def h_M(_μₓ, _μᵥ):
## setpoint on state: h_M(μₓ) = μₓ
## return μₓ ## shape (C,)
## setpoint on observation: h_M(μₓ) = g_M(μₓ)
return g_M(_μₓ, _μᵥ) ## shape (D,)
def dh_M___dμₓ(_μₓ, _μᵥ):
"""
Jacobian of h_M with respect to μₓ.
Since h_M = g_M, this is identical to dg_M___dμₓ.
"""
C3 = θˣ_x['C3']
return np.array([[1.0 / C3]])
## def dg_M___da(_μₓ, _a): ## direct action on observation (rare)
## ## C is a matrix mapping action to observation
## return C ## shape: (D, control_dim)#### run
_a = np.zeros((T, A)) ## action vector
_xˣ = np.zeros((T, C)) ## true state vector
_vˣ = np.zeros((T, B)) ## exogenous force vector
_y = np.zeros((T, D)) ## observation vector
_μ_x = np.zeros((T, C))
setpoint = 15.
## _v = np.ones((T, C)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints
_v = np.ones((T, D)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints
## _μ_v = np.zeros((T, C)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints; static, same as _v
_μ_v = np.zeros((T, D)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints; static, same as _v
_μ_y = np.zeros((T, D)) ## expectation (belief) about y
_ϵ_x = np.zeros((T, C))
_ϵ_y = np.zeros((T, D))
## _ϵ_v = np.zeros((T, C))
_ϵ_v = np.zeros((T, D))
F = np.zeros(T) ## VFE
_dF___dμₓ = np.zeros((T, C))
_dF___da = np.zeros((T, A))
_a[0] = [0.] ## a5 [A]
_xˣ[0] = [10., 7.] ## xˣq3 [C]
_vˣ[0] = [0.] ## vˣv7 [A]
_y[0] = [0.] ## yq3 [V]
_μ_x[0] = [15., 10.] ## μ_xq3, μ_xCharge
_μ_v[0] = [10.] ## μ_vSf7
_μ_y[0] = g_M(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0]) ## μ_yVoltage
## _ϵ_x[0] = _μ_x[0] - f_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[0], _v=_μ_v[0]) ## initial model prediction error
_ϵ_x[0] = _μ_x[0] - f_M(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0]) ## initial model prediction error; pass in vˣ
_ϵ_v[0] = h_M(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0]) - _v[0]
_ϵ_y[0] = _y[0] - g_M(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0]) ## initial sensory prediction error
## state precision
## _λ_x = [10.]
## _λ_x = [0.2, 0.2]
_Π_x = np.diag([.05] * C)
## _Π_x = np.diag([10.0, 10.0])
## setpoint precision
## _λ_v = [50.0]
_Π_v = np.diag([150.0])
## _Π_v = np.diag([50.0, 50.0])
## observation precision
## _λ_y = [10.0]
_Π_y = np.diag([1.0])
## _Π_y = np.diag([10.0, 10.0])
κ = .00005 ## 0.05 ## learning rate (perception)
κₐ = .00005 ## 0.010 ## learning rate (action)
## F[0] = 0.5 * ( _λ_y * _ϵ_y[0]**2 + _λ_x * _ϵ_x[0]**2 + np.log(_λ_y**-1 * _λ_x**-1) )
## F[0] = 0.5*(
## sum( _λ_y[d] * _ϵ_y[0][d]**2 + np.log(_λ_y[d]**-1) for d in range(D) ) +\
## sum( _λ_x[c] * _ϵ_x[0][c]**2 + np.log(_λ_x[c]**-1) for c in range(C) ) +\
## sum(_λ_v[d] * (_μ_y[0][d] - _v[0][d])**2 for d in range(D)) ## for setpoint
## )
F[0] = 0.5 * ( ## numerically more stable with log, log(1/x) = -log(x); act only on the diag elements to avoid divide-by-zero RuntimeWarnings
np.sum(_Π_y @ (_ϵ_y[0]**2)) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_y))) +
np.sum(_Π_x @ (_ϵ_x[0]**2)) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_x))) +
np.sum(_Π_v @ (_ϵ_v[0]**2)) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_v)))
)
## F[0] = 500_000 ## plot looks better
sources_agt_wout = {
# 'v7': f_pulses,
# 'v7': f_lines,
'v7': f_cos,
}
# v7_theta_agt_wout = {
# 'amps' : [7., -1., -3, 10],
# 't_ons' : [0., 1000, 2000, 5000],
# 't_offs': [1000, 2000, 5000, 1e10],
# }
# v7_theta_agt_wout = {
# 'y_pts': [20, -3, -9, 10],
# 't_pts' : [0., 2500, 5000, 10000],
# }
v7_theta_agt_wout = {
'A': .5,
'θ1': .003,
}
for t in range(T - 1):
_vˣ[t+1] = sources_agt_wout['v7'](ts[t], **v7_theta_agt_wout) ## vˣ[t+1] estimated by using current observation from a sensor
#### NEXT STATE
_ẋ = f_E(_xˣ[t], _vˣ[t], _a[t]) + _ω_x[t]
_xˣ[t+1] = _xˣ[t] + _ẋ*Δt
#### OBSERVE
_y[t+1] = g_E(_xˣ[t+1]) + _ω_y[t] ## g is generation function
#### INFER
### A. Calculate VFE gradient wrt μₓ (Eq6.8 ---> Eq6.16)
## _dF___dμₓ[t] = _λ_y * _ϵ_y[t] * dg_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) + \
## _λ_x * _ϵ_x[t] * df_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) + \
## _λ_v * _ϵ_v[t] * dh_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) ## (Eq6.8+setpoint); Eq6.8 contains a minus ??
## _dF___dμₓ[t] = _Π_y @ _ϵ_y[t] @ dg_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) +\
## _Π_x @ _ϵ_x[t] @ df_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) +\
## _Π_v @ _ϵ_v[t] @ dh_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) ## (Eq6.16+setpoint)
_J_obsr = dg_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t], _μ_v[t]) ## Jacobian shape (D,C)
_J_proc = df_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t], _μ_v[t]) ## Jacobian shape (C,C)
_J_setp = dh_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t], _μ_v[t]) ## Jacobian shape (C,C)
_dF___dμₓ[t] = _Π_y @ _ϵ_y[t] @ _J_obsr + _Π_x @ _ϵ_x[t] @ _J_proc + _Π_v @ _ϵ_v[t] @ _J_setp
### A. Calculate VFE gradient wrt a (Eq7.7 ---> )
## _dF___da[t] = _λ_y * _ϵ_y[t] * dy___da(_a[t]) ## Eq7.7 and Eq7.8
## _dF___da[t] = _λ_y * _ϵ_y[t] ## gradient wrt action
_dF___da[t] = (_Π_y @ _ϵ_y[t]) * dy___da(_xˣ[t], _a[t], Δt) ## Eq7.7 and Eq7.8
### B. Define hidden state flow (Eq6.9 ---> Eq6.17)
_μ̇ₓ = -κ*_dF___dμₓ[t]
### B. Define action flows (Eq7.5 ---> Eq7.31)
_ȧ = -κₐ*_dF___da[t] ## Eq7.5
### C. Hidden state & inferred observation update (Eq6.9 ---> Eq6.17); Perception; Euler
_μ_x[t+1] = _μ_x[t] + _μ̇ₓ*Δt ## Perceptual update (gradient descent)
_μ_y[t+1] = g_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _μᵥ=_μ_v[t+1])
### C. Control state update (Eq7.6); Perception; Euler
_a[t+1] = _a[t] + _ȧ*Δt ## (Eq7.6) ## Action update (gradient descent)
## _a[t+1] = np.clip(_a[t+1], -5, 5) ## Clamp action to reasonable range
## _a[t+1] = 0.0 ## comment in to see what happens if no action/control
### D. Recalculate prediction errors (Eq6.6 ---> Eq6.12)
## _ϵ_x[t+1] = _μ_x[t+1] - f_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _v=_μ_v[t+1])
_ϵ_x[t+1] = _μ_x[t+1] - f_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _μᵥ=_μ_v[t+1]) ## # shape (C,); pass in vˣ
_ϵ_y[t+1] = _y[t+1] - g_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _μᵥ=_μ_v[t+1]) ## shape (D,)
## _ϵ_v[t+1] = h_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1]) - _μ_v[t+1] ## shape (C,)
_ϵ_v[t+1] = h_M(_μ_x[t+1], _μ_v[t+1]) - _v[t+1] ## (D,)
### E. Recalculate VFE (Eq6.7 ---> Eq6.15)
## F[t+1] = 0.5*( _λ_y * _ϵ_y[t+1]**2 + _λ_x * ϵ_x[t+1]**2 + np.log(_λ_y**-1 * _λ_x**-1) ) ## Eq6.7
## F[t+1] = 0.5*(
## sum( _λ_y[d] * _ϵ_y[t+1][d]**2 + np.log(_λ_y[d]**-1) for d in range(D) ) +\
## sum( _λ_x[c] * _ϵ_x[t+1][c]**2 + np.log(_λ_x[c]**-1) for c in range(C) ) +\
## sum( _λ_v[d] * (_μ_y[t+1][d] - _v[t+1][d])**2 for d in range(D)) ## for setpoint
## ); #print(f'{F[t+1]=}')
F[t+1] = 0.5*( ## numerically more stable with log, log(1/x) = -log(x); act only on the diag elements to avoid divide-by-zero RuntimeWarnings
np.sum(_Π_y @ _ϵ_y[t+1]**2) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_y))) +
np.sum(_Π_x @ _ϵ_x[t+1]**2) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_x))) +
np.sum(_Π_v @ _ϵ_v[t+1]**2) - np.sum(np.log(np.diag(_Π_v)))
)
result_agt = pd.DataFrame({
't': ts,
'_a_0': _a[:,0],
'_xˣ_0': _xˣ[:,0], '_xˣ_1': _xˣ[:,1],
'_vˣ_0': _vˣ[:,0],
'_y_0': _y[:,0],
'_v_0': _v[:,0],
'_μ_x_0': _μ_x[:,0], '_μ_x_1': _μ_x[:,1],
'_μ_y_0': _μ_y[:,0],
'_ϵ_x_0': _ϵ_x[:,0],
'_ϵ_y_0': _ϵ_y[:,0],
'_dF___dμₓ_0': _dF___dμₓ[:,0],
'_dF___da_0': _dF___da[:,0],
'F': F
})
## print(result_agt.head())def plot_agent_result(result_agt):
ylabel_size = 12
ylabelx = -0.3
ylabely = 0.3
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 18)) ## 2 inches/plot to get height
grid_rows = 8
## gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[1]*grid_rows)
ax = [fig.add_subplot(gs[i]) for i in range(grid_rows)]
for j, axis in enumerate(ax):
axis.grid(True)
axis.set_xlim(0, tT)
locator = MaxNLocator(nbins=5)
axis.xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
axis.spines['top'].set_visible(False); axis.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
if j < grid_rows - 1:
axis.set_xticklabels([]) ## hide labels but keep tick positions
i = 0
ax[i].set_title(
f'Agent\n' + r'(without generalized coordinates)',
fontweight='bold',fontsize=14)
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_a_0'], **styles['a'], label=r'$\mathbf{a}[0]=a_5(t)$: action current [A]')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='A'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_vˣ_0'], **styles['vˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{v}^*[0]=v_7(t)$: true current')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='A'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_xˣ_0'], **styles['xˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[0]=q_3(t)$: true charge')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_x_0'], **styles['μ_x[0]'], label=r'$\boldsymbol{μ}_x[0]$: exp charge')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='C'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_xˣ_1'], **styles['xˣ[1]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[1]=p_6(t)$: true flux [Wb]')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_x_1'], **styles['μ_x[1]'], label=r'$\boldsymbol{μ}_x[1]$: exp flus [Wb]')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='Wb'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_v_0'], **styles['v[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{v}[0]=v(t)$: voltage across C3 setpoint')
## ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_v_0'], **_styles['μ_v'], label=f'$μ_v$: exp outside temperature')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_y_0'], **styles['y[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{y}[0]=y(t)$: obs voltage across C3')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_y_0'], **styles['μ_y[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{μ}_y[0]$: exp voltage across C3')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='V'))
ax[i].legend(loc='lower right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_ϵ_x_0'], color='black', linestyle='-', label=r'$ϵ_{x}$')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_ϵ_y_0'], color='orange', linestyle='-', label=r'$ϵ_{y}$')
ax[i].set_xticklabels([])
ax[i].spines['top'].set_visible(False); ax[i].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='lower left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_dF___dμₓ_0'], color='purple', linestyle='-', label=r'$\frac{dF}{dμ_{x0}}$')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_dF___da_0'], color='cyan', linestyle='-', label=r'$\frac{dF}{da_{0}}$')
ax[i].set_xticklabels([])
ax[i].spines['top'].set_visible(False); ax[i].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['F'], color='red', linestyle='-', label=f'$\cal F$')
ax[i].set_xticklabels([])
ax[i].spines['top'].set_visible(False); ax[i].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
## bottom
ticks = ax[-1].get_xticks()
ax[-1].set_xticks(ticks)
## ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-6*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## micro-seconds
## ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e0*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## seconds
ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-3*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## ms
ax[i].set_xlabel('$\mathrm{Time}\ t\ [\mathrm{seconds}]$', fontweight='bold', fontsize=12)
## plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3) ## Adjust this value as needed
plt.show()
fig.savefig("./ElectricSystem-agent-woutGC", bbox_inches="tight", dpi=300)
## plot_agent_result(result_agt)##
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(filename="ElectricSystem-agent-woutGC-step.png"))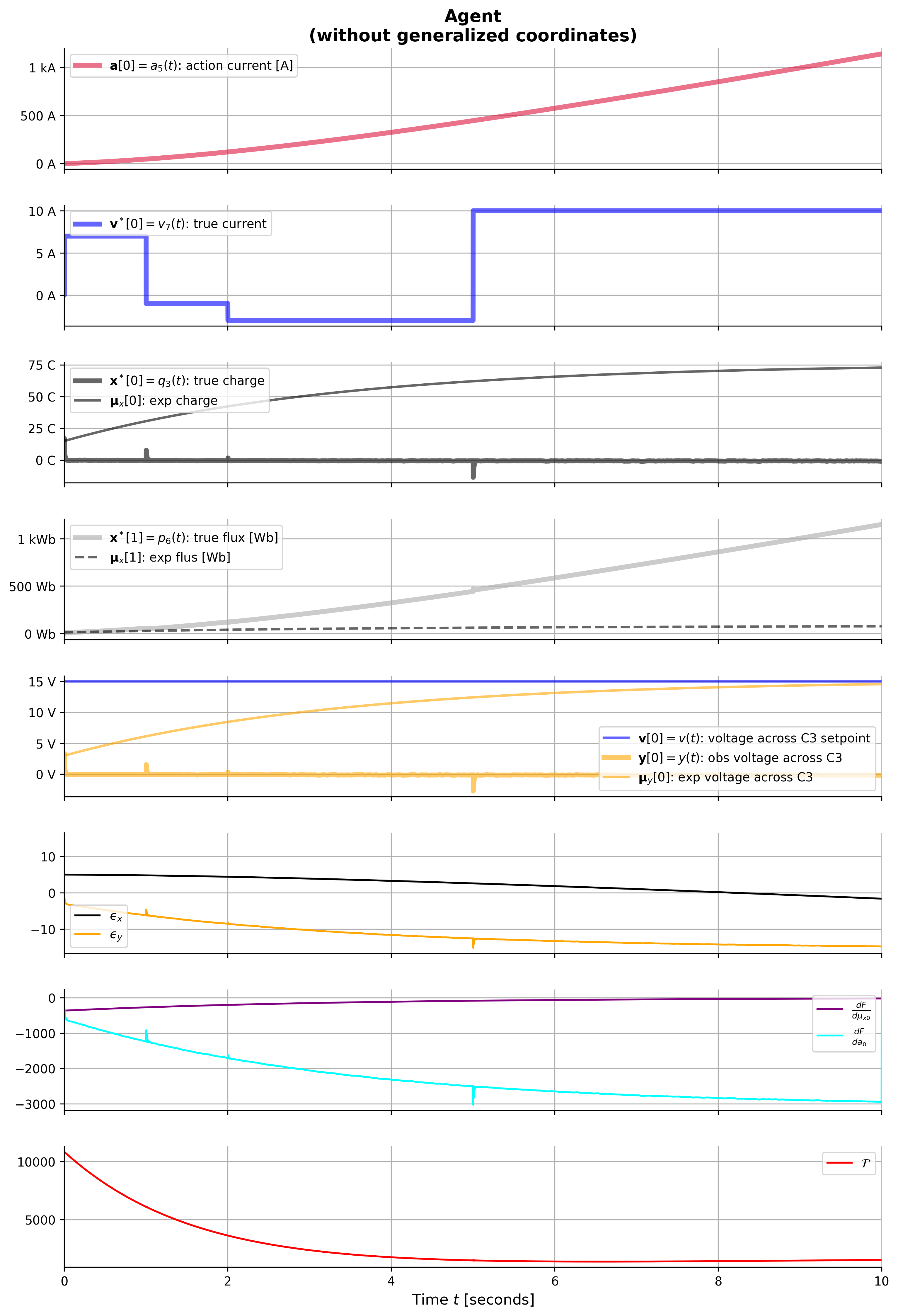
def create_temporal_precision_matrix(M: int, γ: float, σ2: float) -> np.array:
""" Creates a generalized precision matrix
Based on Matlab code from Hijne 2020, pp. 20-21.
Creates a temporal covariance matrix for p+1 orders using a roughness of gamma for
the amount of smoothening. The variance is then used to construct the generalized
precision matrix.
Args:
M (int): The embedding order
γ (float): Roughness parameter
σ2 (float): Variance for x or y (i.e. σ2 * I)
Returns:
_np.array: The generalized precision matrix [M+1, M+1]
"""
## Order of the required autocorrelation derivatives
k = np.arange(0, 2*M+1, 2)
s = np.sqrt(2 / γ)
ρ = np.cumprod(1-k) / (np.sqrt(2) * s)**k
ρ = np.insert(arr=ρ, obj=np.arange(1,len(ρ), 1), values=0)
## Initialize temporal covariance matrix
S = np.zeros((M+1, M+1))
## Loop over all rows of embedding order and population
for r in range(0, M+1):
S[r] = ρ[r:r+M+1]
ρ = -ρ # Inverse rho to alternate minus signs
## Compute generalized precision matrix
Π̃ = np.linalg.inv(np.kron(S, σ2))
##. replace zeros and negative values with a small positive number instead of zero;
##. for np.log() on the elements later
for i in range(Π̃.shape[0]):
for j in range(Π̃.shape[1]):
if Π̃[i,j] <= 0:
Π̃[i,j] = 1e-10 ##. small positive number instead of zero; for np.log()
return Π̃
def D_operator(M):
return np.insert(np.insert(np.eye(M), 0, 0, axis=1), M, 0, axis=0)
## Works for C=1 (scalar state) and any C>1 without changes.
## Avoids any fixed indices like [_\mu_v[0], _\mu_v[3]]
## Lets you later change the initialization (e.g. mix \mu_x and \mu_v) by only modifying
## the two lines that set _\mu_x_embedding[0, :] and [1, :], without touching the shape
### logic
def embed_μ_x(_μ_x, _μ_v, M, C):
"""
Embed state belief μ_x into generalized coordinates up to order M.
_μ_x : array_like, shape (C,)
Current state belief.
_μ_v : array_like, shape (C,) or (D,) depending on your convention.
Here we only use the components you choose to initialise with.
M : int
Highest generalized order (0..M).
C : int
State dimension.
"""
_μ_x = np.asarray(_μ_x).reshape(C,) ## ensure shape (C,)
_μ_v = np.asarray(_μ_v).reshape(-1,) ## 1‑D
## Process model and Jacobian
_f = f_M(_μ_x, _μ_v) ## shape (C,)
_fp = df_M___dμₓ(_μ_x, _μ_v) ## shape (C, C)
## Allocate embedding: rows = generalized order, cols = state components
_μ_x_embedding = np.zeros((M + 1, C))
## 0th generalized coordinate: current state belief
_μ_x_embedding[0, :] = _μ_x
## 1st generalized coordinate: state velocity
_μ_x_embedding[1, :] = _f
## Higher‑order generalized coordinates: successive applications of Jacobian
for i in range(2, M + 1):
_μ_x_embedding[i, :] = _fp @ _μ_x_embedding[i - 1, :]
return _μ_x_embedding
def embed_y(_y, _x, _v, M, C, D):
_f = f_M(_x, _v)
_fp = df_M___dμₓ(_x, _v)
_g = g_M(_x, _v)
_gp = dg_M___dμₓ(_x, _v)
_x_embedding = np.zeros((M+1, C))
_y_embedding = np.zeros((M+1, D))
_x_embedding[0] = _f
for i in range(1, M+1): ## propagate with Jacobian for higher-order terms
_x_embedding[i] = _fp @ _x_embedding[i-1]
_y_embedding[0] = _g
for i in range(1, M+1):
_y_embedding[i] = _gp @ _x_embedding[i-1]
return _y_embedding
def embed_func(func, dfunc, _μ̃_x, _μ_v, dim):
M = _μ̃_x.shape[0] - 1
_func_vec = np.zeros((M+1, dim))
_motion_vec = np.ones((M+1, dim))
_func_vec[0] = 1
_motion_vec[0] = 0
_jac = dfunc(_μ̃_x[0], _μ_v) ## shape (C, C)
## Apply Jacobian to each embedded coordinate
_motion_term = np.array([_jac @ _μ̃_x[m] for m in range(M+1)]) ## (M+1, C)
_f̃ = _func_vec * func(_μ̃_x[0], _μ_v[0]) + _motion_term
return _f̃#### run
## tuning very sensitive to κ, λ_x, λ_y
_a = np.zeros((T, A)) ## action vector
_xˣ = np.zeros((T, C)) ## true state vector
_vˣ = np.zeros((T, B)) ## exogenous force vector
_y = np.zeros((T, D)) ## observation vector
_ỹ = np.zeros((T, M+1, D)) ## generalized sensory input
_μ_x = np.zeros((T, C))
_μ̃_x = np.zeros((T, M+1, C)) ## generalized expectation of x
setpoint = 15.
## _v = np.ones((T, C)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints
_v = np.ones((T, D)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints
_μ_v = np.ones((T, D)) * [setpoint] ## setpoints; static, same as _v
_μ̃_v = np.zeros((T, M+1, D)) ## generalized expected or 'desired' hidden state
_μ_y = np.zeros((T, D)) ## expectation (belief) about y
_μ̃_y = np.zeros((T, M+1, D)) ## NEW
## _ϵ_x = np.zeros((T, C))
## _ϵ_y = np.zeros((T, D))
_ϵ̃_x = np.zeros((T, M+1, C))
_ϵ̃_v = np.zeros((T, M+1, D))
_ϵ̃_y = np.zeros((T, M+1, D)) ## Generalized p.e. [t, 2(M+1), 1]
F = np.zeros(T) ## VFE
## _dF___dμₓ = np.zeros((T, C))
_dF___dμ̃ₓ = np.zeros((T, M+1, C))
_dF___da = np.zeros((T, A))
_a[0] = [0.] ## a5 [A] ///aRoomTemperature [C]
_xˣ[0] = [10., 7.] ## xˣq3 [C], xˣp6 [Wb] ///xˣRoomTemperature [C]
_vˣ[0] = [0.] ## vˣv7 [A] ///vˣOutdoorTemperature [C]
_y[0] = [0.] ## yq3 [V] ///yq3 [C]
_ỹ[0] = embed_y(_y=_y[0], _x=_xˣ[0], _v=_vˣ[0], M=M, C=C, D=D)
## _μ_x[0] = [15, 7] ## initial state belief (before seeing data)
_μ_x[0] = [15., 10.] ## μ_xRoomTemperature ## initial state belief (before seeing data)
## _μ_v[0] = [10, 15]
_μ_v[0] = [10] ## μ_vOutdoorTemperature
_μ̃_x[0] = embed_μ_x(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0], M, C); print(f'{_μ̃_x[0]=}')
_μ_y[0] = g_M(_μ_x[0], _μ_v[0]) ## μ_yRoomTemperature ## initial observation belief (before seeing data)
Dop = D_operator(M); print(f'{Dop=}') ## D operator for _M = 3
## _ϵ_x[0] = _μ_x[0] - f_M(_μ_x[0]) ## initial model prediction error
## _ϵ_y[0] = _y[0] - g_M(_μ_x[0]) ## initial sensory prediction error
_ϵ̃_x[0] = Dop @ _μ̃_x[0] - embed_func(f_M, df_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[0,:], _μ̃_v[0,:], C)
## _ϵ̃_v[0] = Dop @ _μ̃_x[0] - embed_func(h_M, dh_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[0,:], _μ̃_v[0,:], C)
_ϵ̃_v[0] = _ỹ[0] - _μ̃_v[0]
_ϵ̃_y[0] = _ỹ[0] - embed_func(g_M, dg_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[0], _μ̃_v[0], D)
γ_x = 1e4 ## roughness x
γ_y = 1e4 ## roughness y
γ_v = 1e4 ## roughness v
λ_x = .5 ## Prior precision
## _Π_x = np.diag([10.0])
λ_y = .5 ## Likelihood precision
## _Π_y = np.diag([10.0])
λ_v = .5 ## .5 ## Setpoint precision
_Π̃_x = create_temporal_precision_matrix(M=M, γ=γ_x, σ2=1/λ_x)
_Π̃_y = create_temporal_precision_matrix(M=M, γ=γ_y, σ2=1/λ_y)
_Π̃_v = create_temporal_precision_matrix(M=M, γ=γ_v, σ2=1/λ_v)
κ = 1 ## 1 .01 .1 1 ## learning rate (perception)
κₐ = 5e-5 ## 5e-5 .00005 .00001 0.010 ## learning rate (action)
Π_v0 = .64 ## .64 .1 ## tuning scalar
F[0] = 0.5 * ( ## Eq6.55+actions
sum(
_Π̃_y[m, d] * _ϵ̃_y[0][m, d]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_y[m, d])
for d in range(D)
for m in range(M+1)
) +
sum(
_Π̃_x[m, c] * _ϵ̃_x[0][m, c]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_x[m, c])
for c in range(C)
for m in range(M+1)
) +
sum(
_Π̃_v[m, c] * _ϵ̃_v[0][m, c]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_v[m, c])
for c in range(D) ## D, not C; v is preferred observation, not state
for m in range(M+1)
)
)
## F[0] = 100 ## makes plot look better
sources_agt_with = {
# 'v7': f_pulses,
# 'v7': f_lines,
'v7': f_cos,
}
# v7_theta_agt_with = {
# 'amps' : [7., -1., -3, 10],
# 't_ons' : [0., 1000, 2000, 5000],
# 't_offs': [1000, 2000, 5000, 1e10],
# }
# v7_theta_agt_with = {
# 'y_pts': [20, -3, -9, 10],
# 't_pts' : [0., 2500, 5000, 10000],
# }
v7_theta_agt_with = {
'A': .5,
'θ1': .003,
}
for t in range(T - 1):
_vˣ[t+1] = sources_agt_with['v7'](ts[t], **v7_theta_agt_with) ## vˣ[t+1] estimated by using current observation from a sensor
#### NEXT STATE
_ẋ = f_E(_xˣ=_xˣ[t], _vˣ=_vˣ[t], _a=_a[t]) + _ω_x[t]
_xˣ[t+1] = _xˣ[t] + _ẋ*Δt
#### OBSERVE
_y[t+1] = g_E(_xˣ[t+1]) + _ω_y[t] ## g is generation function
#### INFER
### A. Calculate VFE gradient wrt μₓ (Eq6.8 ---> Eq6.16 ---> Eq6.62 and 6.63)
## _dF___dμₓ[t] = _Π_y @ _ϵ_y[t] @ dg_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t]) + _Π_x @ _ϵ_x[t] @ df_M___dμₓ(_μ_x[t])
Dop = D_operator(M)
_dϵ̃___dμ̃_x = C*Dop - np.sum(df_M___dμₓ(_μ̃_x[t+1, 0, :], _μ̃_v[t+1, 0, :])) * np.eye(M+1)
_dϵ̃___dμ̃_y = np.sum(dg_M___dμₓ(_μ̃_x[t+1, 0, :], _μ̃_v[t+1, 0, :])) * np.eye(M+1)
# /////////////////////////////////////
## _dF___dμ̃ₓ[t] = _dϵ̃___dμ̃_x.T @ _Π̃_x @ _ϵ̃_x[t] - _dϵ̃___dμ̃_y.T @ _Π̃_y @ _ϵ̃_y[t] ## Eq6.63
alpha_v_state = 2e-3 ## 2e-3 1e-3 # start very small
dh = np.sum(dh_M___dμₓ(_μ̃_x[t,0,:], _μ̃_v[t,0,:])) ## scalar ∂h/∂μ_x
_dϵ̃_v_dμ̃x = dh * np.eye(M+1) # (M+1, M+1)
_dF___dμ̃ₓ[t] = ( ## Eq6.63
_dϵ̃___dμ̃_x.T @ _Π̃_x @ _ϵ̃_x[t]
- _dϵ̃___dμ̃_y.T @ _Π̃_y @ _ϵ̃_y[t]
+ alpha_v_state * (_dϵ̃_v_dμ̃x.T @ _Π̃_v @ _ϵ̃_v[t])
)
# \\\\\\\
### A. Calculate VFE gradient wrt a (Eq7.7 ---> )
# /////////////////////////////
## _dF___da[t] = _λ_y * _ϵ_y[t] * dy___da(a[t]) ## Eq7.7 and Eq7.8
eps_y_gen = _ϵ̃_y[t, :, 0] ## (M+1,)
w_eps_y = _Π̃_y @ eps_y_gen ## (M+1,)
dF_da_y = w_eps_y[0] * dy___da(_xˣ[t], _a[t], Δt) ## scalar
eps_v0 = _μ_y[t, 0] - _v[t, 0] ## scalar
dF_da_v = Π_v0 * eps_v0 * dy___da(_xˣ[t], _a[t], Δt) ## scalar
_dF___da[t] = np.array([dF_da_y + dF_da_v]) ## shape (1,)
# \\\\\\\\\\
### B. Define hidden state flow (Eq6.9 ---> Eq6.17 ---> Eq6.64)
## _μ̇ₓ = κ*_dF___dμₓ[t]
_μ̃̇ₓ = Dop @ _μ̃_x[t] - κ*_dF___dμ̃ₓ[t] ## Eq6.64
### B. Define action flows (Eq7.5 ---> Eq7.31)
_ȧ = -κₐ*_dF___da[t] ## Eq7.5
### C. Hidden state & inferred observation update (Eq6.9 ---> Eq6.17 ---> Eq6.66); Perception; Euler
## _μ_x[t+1] = _μ_x[t] + _μ̇ₓ*_Δt
## _μ_y[t+1] = g_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _v=_μ_v[t+1])
_μ̃_x[t+1] = _μ̃_x[t] + _μ̃̇ₓ * Δt ## Eq6.66
_ỹ[t+1] = embed_y(_y=_y[t+1], _x=_xˣ[t+1], _v=_vˣ[t+1], M=M, C=C, D=D)
_μ_x[t+1] = _μ̃_x[t+1, 0]
_μ_y[t+1] = g_M(_μ_x[t+1], _μ_v[t+1])
### C. Action update (Eq7.6); Perception; Euler
_a[t+1] = _a[t] + _ȧ*Δt ## (Eq7.6) ## Action update (gradient descent)
## _a[t+1] = np.clip(_a[t+1], -5, 5) ## Clamp action to reasonable range
## _a[t+1] = 0.0 ## comment in to see what happens if no action/control
### D. Recalculate prediction errors (Eq6.6 ---> Eq6.12 ---> Eq6.56 and 6.57)
## _ϵ_x[t+1] = _μ_x[t+1] - f_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _v=_μ_v[t+1])
## _ϵ_y[t+1] = _y[t+1] - g_M(_μₓ=_μ_x[t+1], _v=_μ_v[t+1])
_ϵ̃_x[t+1] = Dop @ _μ̃_x[t+1] - embed_func(f_M, df_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[t+1], _μ̃_v[t+1], C)
_ϵ̃_y[t+1] = _ỹ[t+1] - embed_func(g_M, dg_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[t+1], _μ̃_v[t+1], D)
# ////////////////////////////////
## _ϵ̃_v[t+1] = Dop @ _μ̃_x[t+1] - embed_func(h_M, dh_M___dμₓ, _μ̃_x[t+1,:], _μ̃_v[t+1,:], C)
## generalized desired observation (here only order 0 non-zero)
_μ̃_v[t+1, 0, 0] = _v[t+1, 0] # 15°C trajectory # desired temperature
_μ̃_v[t+1, 1:, 0] = 0.0
_ϵ̃_v[t+1] = _μ̃_y[t+1] - _μ̃_v[t+1] # belief about y vs desired y, all orders
## To make this meaningful, also maintain a generalized belief over y:
## (can refine higher orders later if needed).
_μ̃_y[t+1, 0, 0] = _μ_y[t+1, 0]
_μ̃_y[t+1, 1:, 0] = 0.0
# \\\\\\\\
### E. Recalculate VFE (Eq6.7 ---> Eq6.15 ---> Eq6.55 or Eq6.75)
F[t+1] = 0.5 * ( ## Eq6.55+actions
sum(
_Π̃_y[m, d] * _ϵ̃_y[t+1][m, d]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_y[m, d])
for d in range(D)
for m in range(M+1)
) +
sum(
_Π̃_x[m, c] * _ϵ̃_x[t+1][m, c]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_x[m, c])
for c in range(C)
for m in range(M+1)
) +
sum(
_Π̃_v[m, c] * _ϵ̃_v[t+1][m, c]**2 + np.log(_Π̃_v[m, c])
for c in range(D) ## D, not C; v is preferred observation, not state
for m in range(M+1)
)
)
result_agt = pd.DataFrame({
't': ts,
'_a_0': _a[:,0],
'_xˣ_0': _xˣ[:,0], '_xˣ_1': _xˣ[:,1],
'_vˣ_0': _vˣ[:,0],
'_y_0': _y[:,0],
'_v_0': _v[:,0],
'_μ_x_0': _μ_x[:,0], '_μ_x_1': _μ_x[:,1],
'_μ_v_0': _μ_v[:,0],
'_μ_y_0': _μ_y[:,0],
'_μ̃_x_1_0': _μ̃_x[:,1,0],
'_μ̃_x_2_0': _μ̃_x[:,2,0],
'_μ̃_x_3_0': _μ̃_x[:,3,0],
'_ϵ̃_x_0_0': _ϵ̃_x[:,0,0],
'_ϵ̃_y_0_0': _ϵ̃_y[:,0,0],
'_dF___dμ̃ₓ_0_0': _ϵ̃_x[:,0,0],
'F': F
})
print(result_agt.head())_μ̃_x[0]=array([[ 15. , 10. ],
[ 0. , -3. ],
[ -3. , 6. ],
[ 6. , -11.4]])
Dop=array([[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
t _a_0 _xˣ_0 _xˣ_1 _vˣ_0 _y_0 _v_0 _μ_x_0 \
0 0.0 0.000000 10.000000 7.000000 0.000000 0.000000 15.0 15.000000
1 0.5 0.026701 13.501166 -0.999645 0.500000 2.699231 15.0 23.699674
2 1.0 0.055829 12.738645 -0.820760 0.499999 2.545976 15.0 13.832820
3 1.5 0.081000 12.050651 -0.717366 0.499998 2.408202 15.0 15.225087
4 2.0 0.107028 11.399415 -0.623636 0.499995 2.277758 15.0 11.613051
_μ_x_1 _μ_v_0 _μ_y_0 _μ̃_x_1_0 _μ̃_x_2_0 _μ̃_x_3_0 _ϵ̃_x_0_0 \
0 10.000000 10.0 3.000000 0.000000 -3.000000 6.000000 -20.000000
1 -11.150326 15.0 4.739935 13.500070 0.001159 6.002000 35.800721
2 2.536249 15.0 2.766564 -13.360288 2.983818 5.998419 -18.432787
3 -3.816942 15.0 3.045017 1.959833 5.991834 6.000262 9.593717
4 -0.450691 15.0 2.322610 -2.246027 8.983437 5.999302 -1.344645
_ϵ̃_y_0_0 _dF___dμ̃ₓ_0_0 F
0 -4.000000 -20.000000 38.832778
1 -6.779636 35.800721 464.524867
2 -2.985399 -18.432787 96.676590
3 -3.679905 9.593717 5.545094
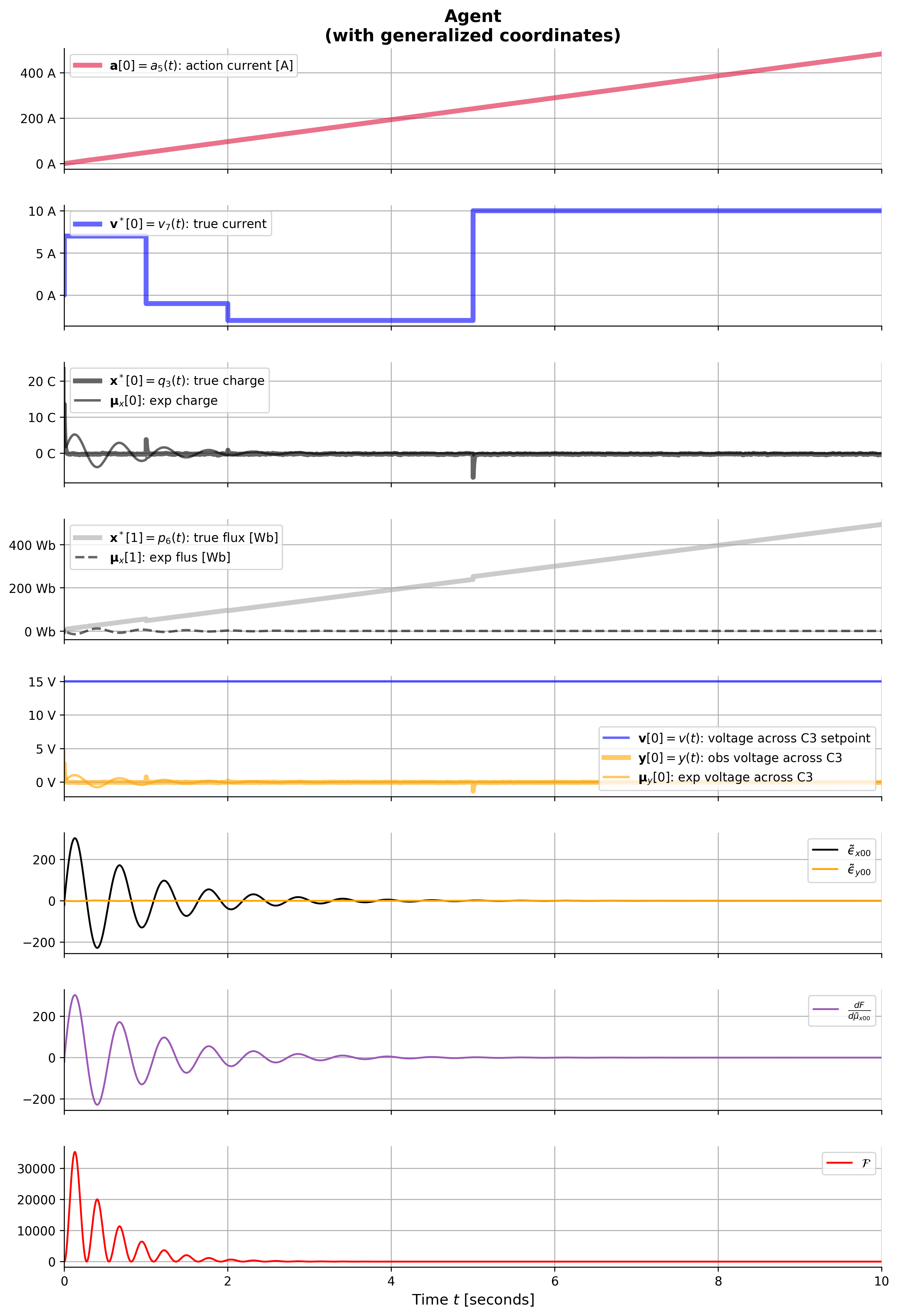
4 -2.365337 -1.344645 -31.396504 def plot_agent_result(result_agt):
ylabel_size = 12
ylabelx = -0.3
ylabely = 0.3
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 18)) ## 2 inches/plot to get height
grid_rows = 8
## gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
gs = GridSpec(grid_rows, 1, figure=fig, height_ratios=[1]*grid_rows)
ax = [fig.add_subplot(gs[i]) for i in range(grid_rows)]
for j, axis in enumerate(ax):
axis.grid(True)
axis.set_xlim(0, tT)
locator = MaxNLocator(nbins=5)
axis.xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
axis.spines['top'].set_visible(False); axis.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
if j < grid_rows - 1:
axis.set_xticklabels([]) ## hide labels but keep tick positions
i = 0
ax[i].set_title(
f'Agent\n' + r'(with generalized coordinates)',
fontweight='bold',fontsize=14)
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_a_0'], **styles['a'], label=r'$\mathbf{a}[0]=a_5(t)$: action current [A]')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='A'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_vˣ_0'], **styles['vˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{v}^*[0]=v_7(t)$: true current')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='A'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_xˣ_0'], **styles['xˣ[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[0]=q_3(t)$: true charge')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_x_0'], **styles['μ_x[0]'], label=r'$\boldsymbol{μ}_x[0]$: exp charge')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='C'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_xˣ_1'], **styles['xˣ[1]'], label=r'$\mathbf{x}^*[1]=p_6(t)$: true flux [Wb]')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_x_1'], **styles['μ_x[1]'], label=r'$\boldsymbol{μ}_x[1]$: exp flus [Wb]')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='Wb'))
ax[i].legend(loc='upper left')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_v_0'], **styles['v[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{v}[0]=v(t)$: voltage across C3 setpoint')
## ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_v_0'], **_styles['μ_v'], label=f'$μ_v$: exp outside temperature')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_y_0'], **styles['y[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{y}[0]=y(t)$: obs voltage across C3')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_μ_y_0'], **styles['μ_y[0]'], label=r'$\mathbf{μ}_y[0]$: exp voltage across C3')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.EngFormatter(unit='V'))
ax[i].legend(loc='lower right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_ϵ̃_x_0_0'], color='black', linestyle='-', label=r'$ϵ̃_{x00}$')
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_ϵ̃_y_0_0'], color='orange', linestyle='-', label=r'$ϵ̃_{y00}$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['_dF___dμ̃ₓ_0_0'], color='#9b59b6', linestyle='-', label=r'$\frac{dF}{dμ̃_{x00}}$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
i += 1
ax[i].plot(result_agt['t'], result_agt['F'], color='red', linestyle='-', label=f'$\cal F$')
ax[i].yaxis.set_label_coords(ylabelx, ylabely)
ax[i].legend(loc='upper right')
## bottom
ticks = ax[-1].get_xticks()
ax[-1].set_xticks(ticks)
## ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-6*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## micro-seconds
# ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e0*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## seconds
ax[-1].set_xticklabels([f"{1e-3*t:.0f}" for t in ticks]) ## ms
ax[i].set_xlabel('$\mathrm{Time}\ t\ [\mathrm{seconds}]$', fontweight='bold', fontsize=12)
## plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3) ## Adjust this value as needed
plt.show()
fig.savefig("./ElectricSystem-agent-withGC", bbox_inches="tight", dpi=300)
## plot_agent_result(result_agt)##
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(filename="ElectricSystem-agent-withGC-step.png"))